2.1 强的松龙纳米微球的特性检测
2.1.1 强的松龙纳米微球的大体形态 图1为筛选最优条件下制备的强的松龙纳米微球粉末大体形态观察,图中可见制得的纳米微球以粉末结晶形式存在,经超声乳化及冷冻干燥机干燥后,纳米微球较分散,有利于下一步其与复合膜的结合。
 图2
图2为强的松龙纳米微球的扫描电镜和透射电镜下照片;从扫描电镜图中可见,强的松龙纳米微球为表面圆滑的球形结构,大体估算及比例尺测量见纳米微球的粒径均匀,分布范围为350-800 nm之间,平均粒径为500 nm,各纳米微球分布均匀;透射电镜照片上可见纳米微球质地均一,无明显的分层现象出现,间接说明药物均匀的分布于纳米微球之中。

2.1.2 强的松龙药物标准曲线的测定
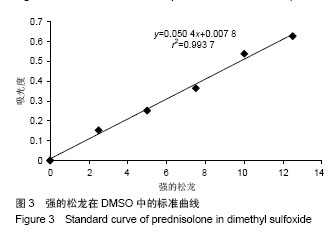
图3为强的松龙在DMSO溶剂中浓度与吸光度相关关系的标准曲线图,图中可见强的松龙标准曲线具有良好的线性关系,方程为y=0.050 4x+0.007 8,
r2=0.993 7(y:吸光度,x:强的松龙浓度,
r2为线性相关系数),由此方程式可以通过测定药物在245 nm处的吸光度值来估计强的松龙药物的浓度。
2.1.3 强的松龙纳米微球的载药量、包封率和体外释药曲线 利用上述载药率及包封率计算公式得出本实验中制得强的松龙纳米微球的载药率和包封率分别为7.67%和89.64%。
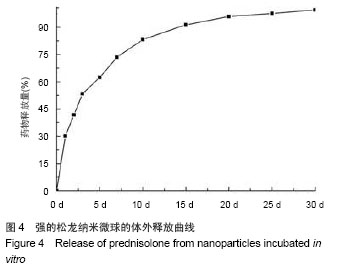
图4为强的松龙纳米微球的体外药物释放曲线,图中可见强的松龙纳米微球实现了药物的缓慢释放,在 30 d内药物释放量达90%以上,缓释效果明显;但是在药物释放的前24 h内药物释放量较大,释药量达30.16%,存在药物突释现象。
2.2 强的松龙在磷脂复合物中的存在状态
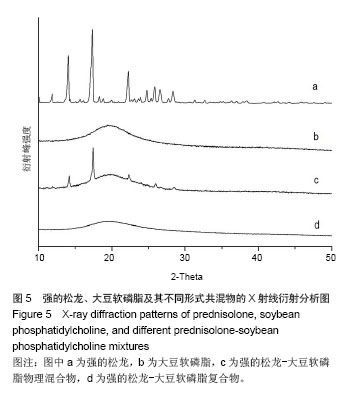
图5为X射线衍射分析分析结果,图中a曲线显示,强的松龙药物主要以晶体形式存在,在10°< 2θ < 25°衍射范围内出现多处强结晶衍射峰;b曲线可见大豆软磷脂无明显结晶衍射峰出现,仅为一条光滑的曲线;c曲线可见强的松龙与大豆软磷脂物理混合后,强的松龙的结晶衍射峰仍然存在,且无新的结晶衍射峰生成,但是强的松龙的各衍射峰值均出现了不同程度的降低,表明大豆软磷脂的加入减弱了强的松龙的晶体存在状态;d曲线可见,强的松龙磷脂复合物中,强的松龙的晶体衍射峰完全消失,只展现出了一条光滑的曲线,与大豆软磷脂的衍射曲线相类似,显示了强的松龙磷脂复合物中强的松龙的存在状态是与大豆软磷脂相结合,而不是以自己本身的晶体状态存在。
 2.3 强的松龙纳米微球缓释膜的形态学考察 图6
2.3 强的松龙纳米微球缓释膜的形态学考察 图6为制得的纳米微球缓释膜的照片,图中可见制得的缓释膜光滑平整,厚度均一,具有较好的柔韧性及吸水性能。
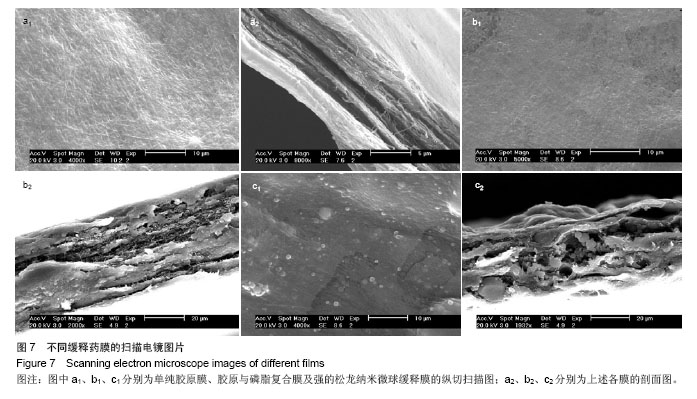
图7为强的松龙缓释药膜不同阶段的扫描电镜图片,其中a
1、b
1、c
1分别为单纯胶原膜、胶原与磷脂复合膜及强的松龙纳米微球缓释膜的纵切扫描图;a
2、b
2、c
2分别为上述各膜的剖面图。从
图a1、
a2中可见,单纯胶原膜表面致密,有大量交错的纤维结构组成,剖面图可见胶原膜内部由层状组织组成,层状组织间有空隙;
图b1、
b2所示为胶原与磷脂的复合膜,图中可见与单纯胶原膜相比磷脂复合膜的表面纤维样组织不明显,质地更加光滑致密,剖面图可见胶原膜层与层之间的空隙被磷脂组织填充,更加光滑致密,使胶原膜的生物学特性更佳,有利于药物的持续缓慢释放。
图c1、
c2为强的松龙纳米微球缓释膜,图中可见少量的纳米微球附着于缓释膜的表面,这与该药膜体外释放试验中少量的药物突释现象有关,剖面图可见胶原与磷脂复合膜的结构未见明显改变,纳米微球均匀分布于复合膜中,周围由磷脂组织填充;由图中可看出,强的松龙药物首先从药膜表面附着的纳米微球中释放,后随着胶原磷脂复合膜的降解,复合膜内部的纳米微球逐渐降解,将药物从膜中释放出来;复合药膜的致密结构有利于纳米微球的持续缓慢释放。
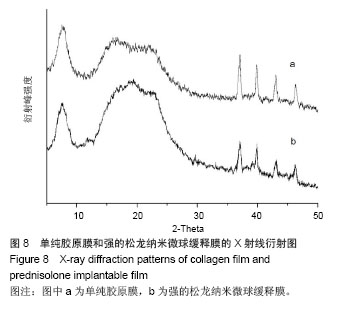
 2.4 强的松龙纳米微球缓释膜的结构分析 图8
2.4 强的松龙纳米微球缓释膜的结构分析 图8可见以胶原膜主要膜材料制成的强的松龙纳米微球缓释膜与单纯胶
原膜相比各衍射峰未见明显改变,各结晶峰值的位置几乎与胶原膜相同,但其结晶强度有所减弱,这说明以胶原作为强的松龙复合膜的主要材料并未改变胶原膜原本的结构,其衍射峰值减弱的原因可能为壳聚糖和软磷脂的加入掩盖了胶原膜部分结晶强度,但胶原膜原本性质未变。
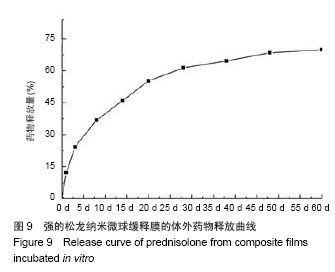
 2.5 强的松龙纳米微球缓释膜体外释药行为 图9
2.5 强的松龙纳米微球缓释膜体外释药行为 图9为强的松龙纳米微球缓释膜的体外药物释放曲线,从图中可见,纳米微球缓释膜在60 d的时间内释放了其载药量的75%,在
30 d时其药物的释放量达到60%以上,具有明显的药物缓释效果,且药物释放量较单纯的纳米微球更加稳定、持久;其中纳米微球缓释膜在最初24 h内药物的释放量为8.06%,未出现明显药物突释现象,与单纯纳米微球相比(
图4),药物释放更加平稳,具有良好的体外药物释放作用。









.jpg)